- Natural Selection.
- Gene flow.
- Genetic drift.
- Mutations.
1) NATURAL SELECTION (SELECCIÓN NATURAL)
Described by Darwin, basically it says that the environment is the one changing (not the organisms), and it is the nature the one that "selects" the best organisms. The steps could be summarized as:
1. Inside populations there is variability, not all the organisms are the same.
2. For a certain environment, some organisms will be best adapted, having advantage, surviving more and reproducing.
3. They will pass their successful characteristics to their offspring.
4. These characteristics will become more frequent in the population.
This is described as the "survival of the fittest". But the environment changes, and the best adapted in a moment could not be the fittest in other moment.
Descrito por Darwin, básicamente dice que es el ambiente el que cambia (no los organismos), y es la naturaleza la que selecciona a los mejores organismos. Los pasos se podrían resumir:
1. Dentro de las poblaciones hay variedad, no todos los organismos son iguales.
2. Para cierto ambiente, algunos organismos estarán mejor adaptados, teniendo ventaja, sobreviviendo y reproduciendose mas.
3. Estos pasaran sus características exitosas a su descendencia.
4. Estas características se harán mas frecuentes en la población.
Esto se describe como la "supervivencia de los mas aptos". Pero el ambiente cambia, y los mejores adaptados en un momento pueden no ser los mejores adaptados en otro momento.
2) GENE FLOW (FLUJO DE GENES)
It can be summarized as in one stable population new organisms arrive with new characteristics, these characteristics will appear in next generations, changing the percentages of the characteristics.
Puede resumirse como que si en una población estable llegan nuevos organismos con nuevas características, estas características aparecerán en las nuevas generaciones, cambiando los porcentajes de las características.
3) GENETIC DRIFT (DERIVA GENETICA)
When a population is affected by an event totally by chance, so the percentages of the characteristics in the populations are going to change. There are two important types of genetic drift events: the Founder Effect and the Bottleneck Effect.
Cuando una población es afectada por un evento totalmente al azar, los porcentajes de las características en la población van a variar. Hay dos tipos importantes de eventos de deriva genética: el Efecto Fundador y el Efecto Cuello de Botella.
a) FOUNDER EFFECT (EFECTO FUNDADOR)
When a population isolates from others creating a new colony, the new population will be small, so it will have less genetic variation. Some characteristics that in the first population were common could even disappear, or recessive traits in the main population could become frequent in the colony. For example, the six fingers in the Amish population.
Cuando una población se aísla de otras creando una nueva colonia, la nueva población será pequeña,por lo que tendrá menos variación genética. Algunas características que en la primera población eran comunes podrían incluso desaparecer, o rasgos recesivos en la población principal podrían volverse frecuentes en la colonia. Por ejemplo, los seis dedos en la población Amish.
b) BOTTLENECK EFFECT (EFECTO CUELLO DE BOTELLA)
In this case a population decreases (sometimes even near to extinction) due to a random event (hunting, natural disaster...). The population survives with a few individuals, so the variety of genetic variation is low. When the population increases in time, it has lost characteristics which it usually had before the disaster. For example, what happened with sea elephants due to their hunting by human.
En este caso una población disminuye (a veces incluso cerca de la extinción) debido a un suceso al azar (caza, desastre natural...). La población sobrevive con unos pocos individuos, así que la variedad genética es baja. CUando la población se recupera en el tiempo, ha perdido características que solía tener antes del desastre. Por ejemplo, lo que les ocurrió a los elefantes marinos debido a su caza por los humanos.
4) MUTATIONS (MUTACIONES)
Mutations are changes in the DNA. When these mutations affect gametes (sperm and egg cells) and can pass to the offspring, is when they can affect evolution. ANd not always, because we have neutral mutations, positive mutations and negative mutations, and all of them happen randomly.
Las mutaciones son cambios en el DNA. Cuando estas mutaciones afectan a los gametos (espermatozoides y óvulos) y pueden pasar a la descendencia es cuando pueden afectar a la evolución. Y no siempre, porque hay mutaciones neutras, mutaciones positivas y mutaciones negativas, y todas ellas ocurren al azar.

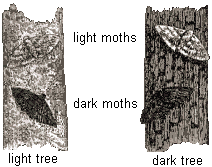



No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario